Performance Analysis
Risk Management

Risk Management
Risk management is crucial to achieving the strategic objectives of the NLB Group. Using standard risk management methods allows for qualitative assessment of all types of risks, presents timely responses, and reduces exposure to risks. NLB and its subsidiaries at first follow the regulations of the Bank of Slovenia, but additional risk management is also internally regulated.
The limits concerning the extent and the variety of risks the NLB Group members are willing to accept in their business operations are expressed by the terms appetite and tolerance for taking risks. The way to control risk for the Bank involves having a clear organizational structure, an effective procedure to manage risk as well as a suitable internal control system. The objective is to reduce any departures from the goal of realizing expected earnings and to minimize damages from operational risks while optimizing the use of regulatory and internal capital. The amount of capital and targeted results are the factors that currently define the framework of the risk appetite.
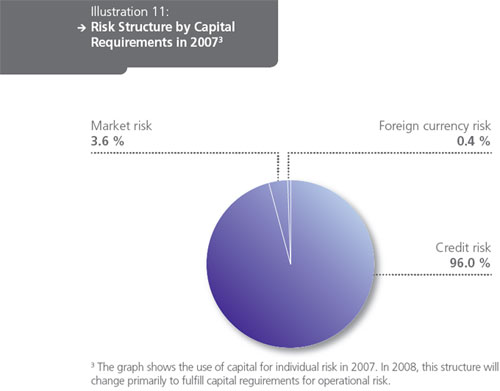
The most important risk in the NLB Group is credit risk, followed by operational risk and market risk. The Bank pays particular attention to these types of risk as it strives to meet its strategic objectives. In the process of evaluating appropriate internal capital, the Bank also focuses on risks that threaten its strategy, reputation, capital and profitability.
In 2007, new legislation on risk management, as well as on calculating capital and capital requirements was adopted in Slovenia in compliance with the provisions of BASEL II. The NLB executed all the necessary activities for the implementation of the new legislation in 2007.
For the implementation of the BASEL II requirements, the Bank selected a standardized approach for the whole group to calculate the required capital for credit risks; a standardized approach to calculate the operating risks for the NLB and a simple approach for the NLB Group.
Credit Risk Management
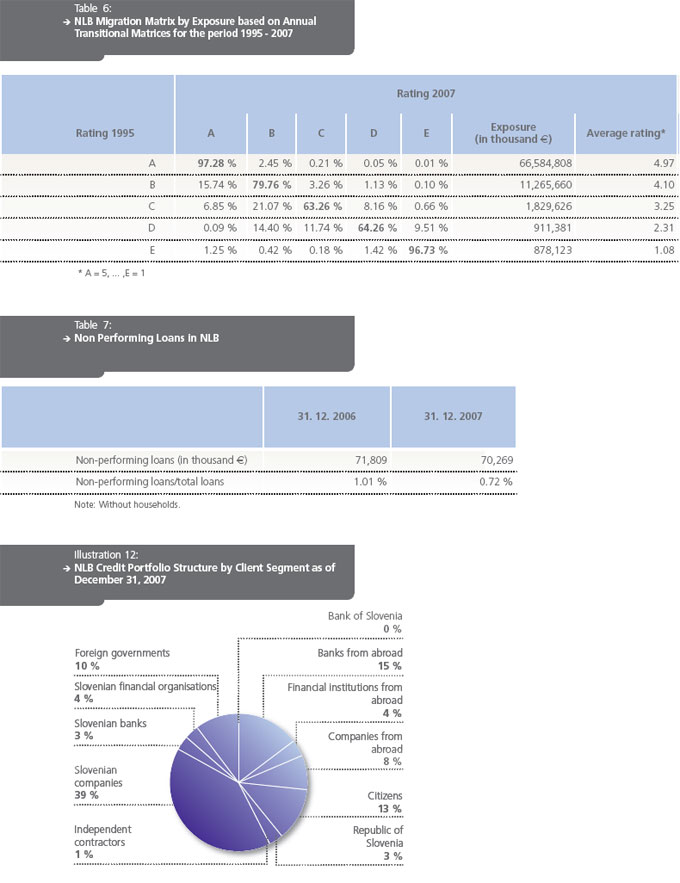
The NLB Group performs risk management on two levels: controlling risks for individual clients, and supervising credit portfolio risks for banks and other members of the NLB Group.
Prior to credit approval and entering into a contract that exposes the bank to a credit risk, every client receives a credit rating and the bank also sets borrowing limits. The clients’ credit rating depends on their financial standing, business record, and ability to provide proof of sufficient cash flow to meet their financial obligations. The bank also checks the clients’ records; the quantity and quality of their current relationship with a bank or financial institution. The credit status of a client, whose headquarters are located abroad, also is influenced by the risk rating of that country. The upper limit of indebtedness depends on the client’s credit rating, investment prospects, and all the other factors that involve repayment of a loan. Depending on the risks involved in a particular deal and evidence of impaired credit, the Bank or its Group member, establishes impairments and reserve provisions in accordance with IFRS. For the bulk of the portfolio, impairments are established on a case-by-case basis after an individual review of the accounts receivable. For the smaller portion of the portfolio, impairments are determined collectively based on historical data.
The credit portfolios of individual members are regularly reviewed by categories (credit rating, country, type and size of client, activity, insurance, non performing/expired receivables, currency exposure etc.). The review includes an analysis of changed status, and is based on time sensitive categories, assessing trends and cycles, risks and concentration of credit portfolios.
One of the more important instruments for reviewing and assessing the quality of the credit portfolio and adequacy of provisions is the rating migration matrix of clients within credit rating categories. Matrices are also good guides and indispensable tools for evaluating the share of potentially non performing accounts receivable in the future and for determining the necessary amount of internal capital required to cover credit risks.
The NLB regularly reviews the business practices and investment portfolios of its members to make sure they operate in accordance with the risk management standards of the NLB Group. This allows the bank to certify uniform practices for managing and reporting credit risks on the consolidated level.
Market Risk Management
In 2007, market risk exposure was relatively insignificant. In compliance with the adopted risk management program within Group, the NLB set up guidelines to monitor market risks. This makes possible a reasonably uniform approach to policies, procedures and methodologies and standardized reporting. Monitoring and managing exposure to market risks of the NLB Group is not centralized, but reports on members exposure to risk are regularly submitted to NLB Group Assets and Liabilities Committee.
In accordance with the regulations of the Bank of Slovenia, the NLB is the only bank which has trading activities within the Group. As such, the NLB is the only bank that is required to ensure adequate capital funds to cover market risks. The other bank members monitor foreign exchange and interest rate risks, primarily the result of structural fluctuations and macroeconomic conditions, by following the NLB Group’s risk management guidelines.
The methodologies comply with the requirements of regulators on an individual and group level, while current reporting to a regulator follows a standardized approach. In compliance with the Bank of Slovenia requirements, the NLB Group provides adequate capital funds to cover potential unexpected losses due to exposure to foreign exchange and other market risks.
Foreign Exchange Risk Management
The NLB regularly monitors exposure to foreign exchange risks for the whole group. The methodology of measuring foreign exchange risks is based on the principle of open currency positions and by monitoring the fulfillment of nominal limits (for the total net open position and per individual currencies).
The bank is conservative in its approach in managing exposure to foreign exchange risks. It minimizes these risks by closing open forex positions within set limits on a daily basis. The bank uses the standardized methodology to calculate currency risks as well as its internal model VAR (Value-at-Risk). Daily calculation of the value of VAR is done in compliance with the requirements of the Basel standards (99% confidence level, 300 business day monitoring period, 10-day holding period) and is based on the historical simulation method. Back testing is performed on a regular basis to verify the accuracy of the model as well as stress scenarios. The model is only used for internal purposes.

Trading Book
The main focus of the NLB trading activities is to provide customer service, asset management and trading for its own account. The bank trades in: currencies, interest rates, securities and derivatives, while its trading in options is limited to forex and interest rate options and is primarily done upon the request of a client.
The bank uses the internal VAR model. The daily-calculated value of VAR complies with the Basel standards (99% confidence level, 250 working days monitoring period, 10-day holding period) and is based on variance-covariance methodology. The model is used to monitor and manage market risks, and compliance with limits is checked daily. In addition, for the purpose of capital adequacy, market risks in the trading book are examined by using the standardized approach.
Interest Rate Risk Management
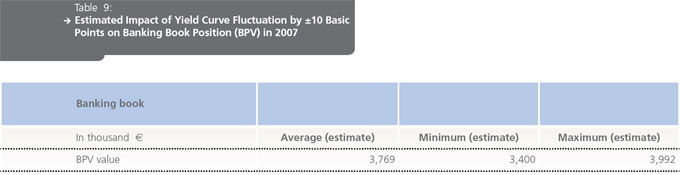
The NLB regularly supervises the exposure to interest rate risks for the whole NLB Group. The bank’s interest rate exposures are monitored and managed using the methodology of interest rate sensitivity gap reports. These reports include the analysis of net interest rate sensitive positions at a single point in time. The bank also performs sensitivity analyses to determine vulnerability to interest rate changes. The BPV (Basis Point Value) method is used to estimate the change in the market value of the bankbook position as the result of the parallel movement of the yield curve by ± 10 basic points (± 0.1%). The BPV method measures the sensitivity of the value of financial instruments applied to market interest rates, that is, the change in required yield (earnings).
Annual Report 2007